Yoga is a group of physical, mental, and spiritual practices or disciplines which originated in ancient India. There is a broad variety of yoga schools, practices, and goals in Hinduism, Buddhism, and Jainism. Among the most well-known types of yoga are Hatha yoga and Rāja yoga.
The origins of yoga have been speculated to date back to pre-Vedic Indian traditions; it is mentioned in the Rigveda, but most likely developed around the sixth and fifth centuries BCE, in ancient India’s ascetic and śramaṇa movements.
The chronology of earliest texts describing yoga-practices is unclear, varyingly credited to Upanishads. The Yoga Sutras of Patanjali date from the first half of the 1st millennium CE, but only gained prominence in the West in the 20th century. Hatha yoga texts emerged around the 11th century with origins in tantra.
Yoga gurus from India later introduced yoga to the West, following the success of Swami Vivekananda in the late 19th and early 20th century. In the 1980s, yoga became popular as a system of physical exercise across the Western world. Yoga in Indian traditions, however, is more than physical exercise; it has a meditative and spiritual core. One of the six major orthodox schools of Hinduism is also called Yoga, which has its own epistemology and metaphysics, and is closely related to Hindu Samkhya philosophy.
Many studies have tried to determine the effectiveness of yoga as a complementary intervention for cancer, schizophrenia, asthma, and heart disease. The results of these studies have been mixed and inconclusive. On December 1, 2016, yoga was listed by UNESCO as an Intangible cultural heritage.
Peaceful Warrior Yoga is a 27 minute practice to soften, strengthen, and remember that your attitude help shapes your world.
Yoga Bioelectrography Research – The Science of Yoga on IUMAB website
Bioelectrography research articles, research PDF, health benefits of statistics, medical benefits
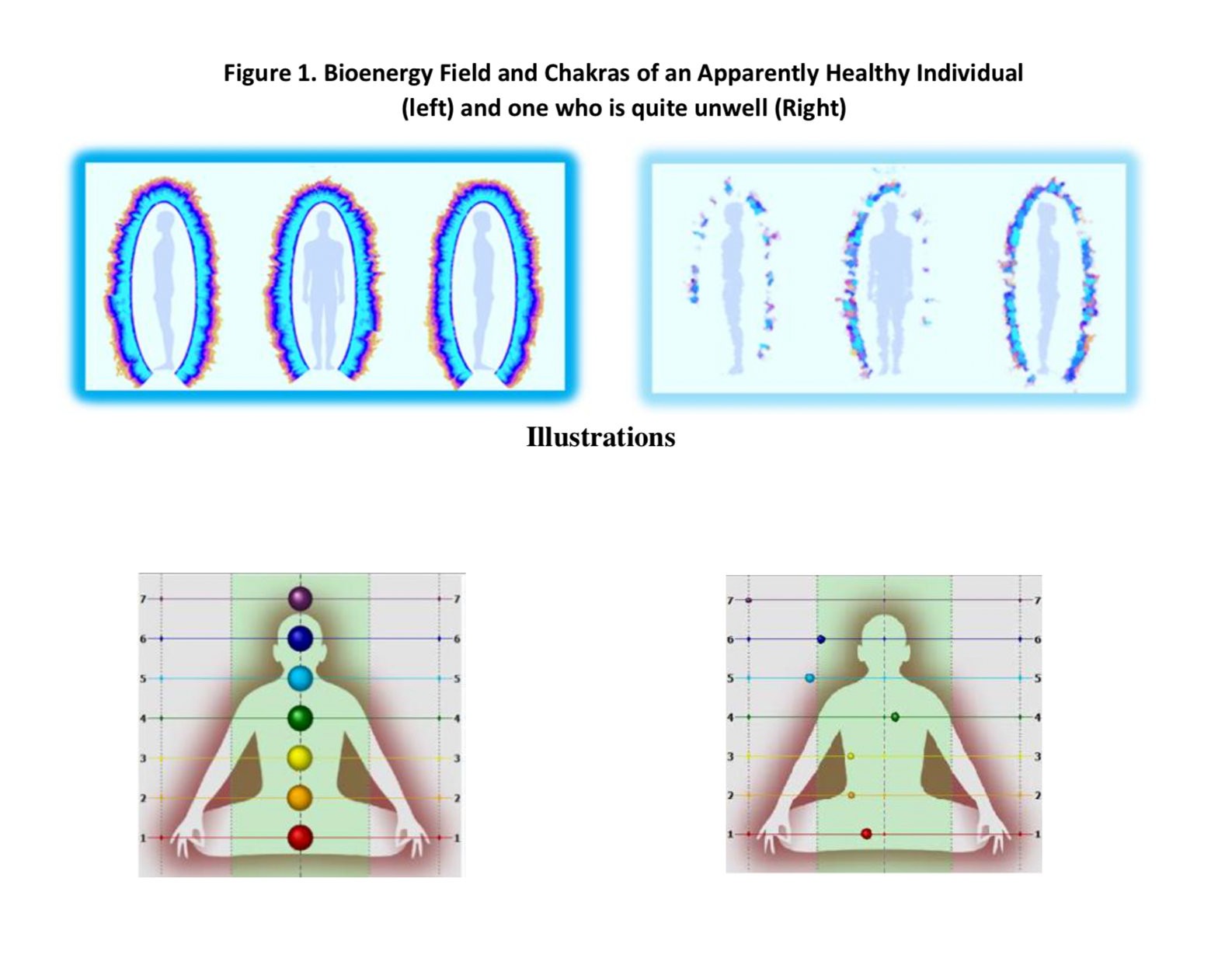
GDV/EPI Reading of Before and After Yoga Session
Diabetes Mellitus Type 2 and Yoga: Electro Photonic Imaging Perspective
By Bhat, Romesh; Mavathur, Ramesh; Srinivasan, T.
Article excerpt
Byline: Romesh. Bhat, Ramesh. Mavathur, T. Srinivasan
Background: Yoga is the most popular form of alternative medicine for the management of diabetes mellitus type
2. The electro-photonic imaging (EPI) is another contribution from alternative medicine in health monitoring. Aim: To evaluate diabetes from EPI perspective.
Objectives: (1) Compare various EPI parameters in normal, prediabetic and diabetic patients. (2) Find difference in controlled and uncontrolled diabetes. (3) Study the effect of 7 days diabetes-specific yoga program. Materials and Methods: For the first objective, there were 102 patients (normal 29, prediabetic 13, diabetic 60).
In the second study, there were 60 patients (controlled diabetes 27, uncontrolled diabetes 33).
The third study comprised 37 patients. EPI parameters were related to general health as well to specific organs.
Results: In the first study, significant difference was observed between (1) Diabetics and normal: average intensity 5.978, form coefficient 3.590, immune organs 0.281 all P < 0.001; (2) Diabetics and prediabetics: average intensity 6.676, form coefficient 4.158, immune organs 5.890 P < 0.032; (3) Normal and prediabetes: immune organs (−6.171 P = 000). In the second study, remarkable difference was in the immune organs (0.201, P = 0.031). In the pre- and post-study, the mean difference was: area 630.37, form coefficient 1.78, entropy 0.03, liver 0.24, pancreas 0.17, coronary vessels 0.11, and left kidney 29, with all P < 0.02.
Conclusion: There is a significant difference in EPI parameters between normal, prediabetics and diabetics, the prominent being average intensity, form coefficient, and immune organs. Between controlled and uncontrolled diabetes, immune organs show significant change. Intervention of yoga results in change in most parameters.
Power of Anapanasathi Meditation – Research using GDVCAMERA
Mathew, an expert in Kirlian Photography (GDV) experiments with Anapanasathi Mediation under Pyramid as taught by Patriji.
He found that this is a unique technique that not only takes care of Physical side (health) but also Spiritual side of development. In this video Mathew shares his research with Patriji and thanks him for bringing this simple, easy and unique technique to the mankind.
See also:
Effect of anapanasati meditation technique through electrophotonic imaging parameters
A pilot study
Article in International Journal of Yoga · December 2015
Power of Anapanasathi Meditation
Kirlian Photography and Kirlian Effect
Kirlian Photography is a process that uses pulsed high voltage frequencies & electron cascades to take pictures of usually invisible, radiating energy fields that surround us all. Photo techniques.
EFFICACY OF INTEGRATED YOGA PRACTICES ON HEALTHY PEOPLE USING ELECTRO PHOTONIC IMAGING TECHNIQUE
Thesis submitted by Kuldeep Kumar Kushwah
Towards the partial fulfilment of DOCTOR OF PHILOSOPHY (YOGA)
UNDER THE GUIDANCE OF T. M. Srinivasan, Ph.D., D.Sc. H. R. Nagendra, Ph.D., D.Sc. Swami
Vivekananda Yoga Anusandhana Samsthana (SVYASA) (Deemed University) # 19, Eknath Bhavan, Gavipuram Circle Kempe Gowda Nagar, Bangalore, 56019 Website: www.svyasa.org
Effect of yoga based techniques on stress and health indices using electrophotonic imaging technique in managers
Kuldeep K. Kushwah,a,∗ Thaiyar M. Srinivasan, b Hongasandra R. Nagendra, and JuduV. Ilavarasua
Abstract
Background
Meditation techniques are known to elicit relaxation response in which moving meditation which combines the practice of yoga postures and guided relaxation is known as Cyclic Meditation reported helpful in reducing the sympathetic arousal and improving health of practitioners.
Objectives
The objective of this study was to investigate the effect of Cyclic Meditation on stress and health indices in managers as measured by Electro Photonic Imaging (EPI) technique.
Materials and methods
EPI technique was used to assess participants before and after 35 min of Cyclic Meditation (CM) and equal duration of Supine Rest (SR) session. A total of sixty six male managers, age ranges from 35 to 60 years (mean ± SD 53.97 ± 5.96) were included in the study. EPI parameters, including Activation Coefficient, Integral Area left and right and Integral Entropy, left and right were taken for statistical analyses.
Results
Cyclic Meditation has produced a highly significant reduction in stress level, whereas this reduction was not found significant within SR group. There was a significant improvement in health index ‘Integral Area’ values in both left and right sides within the CM group while only IA right side showed a significant improvement within the CM group. The integral entropy value right side decreased significantly within the CM group, whereas IE left was found deteriorated within the SR group. Moreover, only IE left side has shown a significant difference between the groups.
Conclusion
The investigations in this study suggest that Cyclic Meditation practice reduces stress and improves psychosomatic health indices more effectively than Supine Rest in managers.
Keywords: Cyclic meditation, Supine rest, Electro photonic imaging technique EPI, Activation coefficient, Integral entropy, Integral area
1. Introduction
ElectroPhotonic Imaging (EPI) technique based on Kirlian effect is a scientific method to assess stress in individuals [1]. The assessment through EPI is performed through stimulation of electrons at the finger tips by applying a short electric pulse of a high voltage (10 kv), high frequency (1024 Hz) and low current for less than a millisecond [2]; then a glow occurs. This glow is the consequence of ionization of gaseous molecules in the surrounding air through the discharged electrons from the finger tips; this glow is captured by a CCD-camera and is known
as electro-photonic image [3]. These EPI images are obtained from all 10 fingers of both the hands in two ways, with filter and without filter. A filter is a specially designed thin plastic film placed between the finger and the dielectric plate during assessment. It eliminates sweat effects due to sympathetic (psychosomatic) responses and obtains only the parasympathetic (or physiological functional state of the person) response [4]. Comparison of these images acquired with and without filter forms a parameter called Activation Coefficient, which is a quantitative
assessment of stress level of a person, based on evaluation of autonomic balance [5]. The experimental data correlating the findings of EPI measures with heart rate variability [6], systolic and diastolic pressures [7] and the stress level [8] suggest that EPI can be used to measure the activity of autonomic responses.
Effect of Integrated Yoga Program on Energy Outcomes as a Measure of Preventive Health Care in Healthy People
Kuldeep Kumar Kushwah,a, b, c, d Hongasandra Ramarao Nagendra,a, d Thaiyar Madabusi Srinivasana, d
S-VYASA University, Bangalore, India A Study Design; B Data Collection; C Statistical Analysis, D Manuscript Preparation
Abstract.
The aim of this study was to measure the changes in stress, general health index and disorderliness in human energy pattern through Integrated Yoga Practices (IYP). Ninety four healthy volunteers (male 55 and female 39), age (mean ± sd 26.70 ±8.58) were assessed before and after four weeks of IYP. The experiment was conducted four times and the assessment was done by utilizing the Electro Photonic Imaging (EPI) technique. Comparisons were made to ascertain whether energy homeostasis diverges based on genders. The parameters considered for analysis were Activation Coefficient (AC), Integral Area (IA) and Integral Entropy (IE).
Reduction
in stress levels (AC), increase in general health index (IA) and
decrease in disorderliness (IE) on the left side parameters were found
reproducible in all four experiments. The results also revealed a highly
significant reduction in stress levels and highly significant
improvement in the health indices at the psycho-physiological level. The
subgroup analysis of both male and female demonstrated a significant
reduction in stress levels and significant improvement in health index
(psycho-physiological). Baseline comparisons between males and females
showed significant difference in general health index at both
psychophysiological and physiological levels.
In conclusion, IYP
regulates, improves and prolongs energy homeostasis of an organism.
Therefore, it helps in prevention of ill health and also preserves
health. The EPI outcomes are reproducible. Further, the present study
also found that the energy pattern differs with gender. Hence, it is
suggested that studies with male and female participants may be
conducted separately.
Key words: Integrated Yoga Program IYP, Electro Photonic Imaging Technique EPI, Gas Discharge Visualization GDV, Stress, General Health Index and Disorderliness
Yoga Bioelectrography Research – The Science of Yoga on IUMAB website




